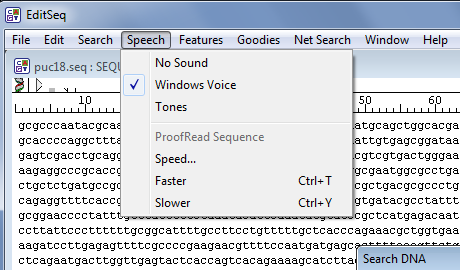
Open Seq File
Welcome to NCBI's Sequence Viewer 3.40.1. To get started, or click on the at the upper right to review the Help documentation. Example Links: Human chromosome: NC000001 This link provides a look at human chromosome 1. SEQ file is a Tinker Archive.Tinker is a software tools for Molecular Design.SEQ file type contains the primary sequence of a biopolymer in the standard one-letter code with 50 residues per line.
- Software that open seq file - DNA sequence data Programs supporting the exension seq on the main platforms Windows, Mac, Linux or mobile. Click on the link to get more information about listed programs for open seq file action.
- How to open SEQ file? After double-clicking on the unknown file icon, the system should open it in the default software that supports it. If this does not happen, download and install the PowerTracks Pro Audio software and then manually associate the file with it.
If you have on your computer a.SEQ file that you cannot open, you are in exactly the same situation as thousands of other people who have similar problems with this or any other unknown file. There may be several reasons why you cannot open the file with.SEQ extension.
- 1.PowerTracks Pro Audio Project File
- 2.DNA Sequence Text File
- 3.NorPix StreamPix Sequence
- 4.Tiertex Limited SEQ Video File
File Type 1PowerTracks Pro Audio Project File
| Developer | PG Music |
| Popularity | |
| Category | Audio Files |
| Format | Binary |
What is a SEQ file?
Audio project created with PowerTracks Pro Audio, a digital audio sequencing program; may include both audio and MIDI tracks, which can be played back at the same time; also stores digital mixer settings, such as track volume, panning, and effects.
SEQ files may also include song structure information, such as verse and chorus sections, as well as key signature and tempo data. MIDI data saved in a SEQ file can be viewed in a piano roll format or as a musical score.
Open over 300 file formats with File Viewer Plus.Programs that open SEQ files
File Type 2DNA Sequence Text File
| Developer | N/A |
| Popularity | |
| Category | Data Files |
| Format | Text |
.SEQ File Association 2
Plain text file that contains a DNA sequence in .FASTA format; often produced by processing an .AB1 file and trimming the low-quality bases from the sequence; therefore, SEQ files are shorter than AB1 files; they can be viewed by most DNA sequencing programs and viewed in a text editor.
Programs that open SEQ files
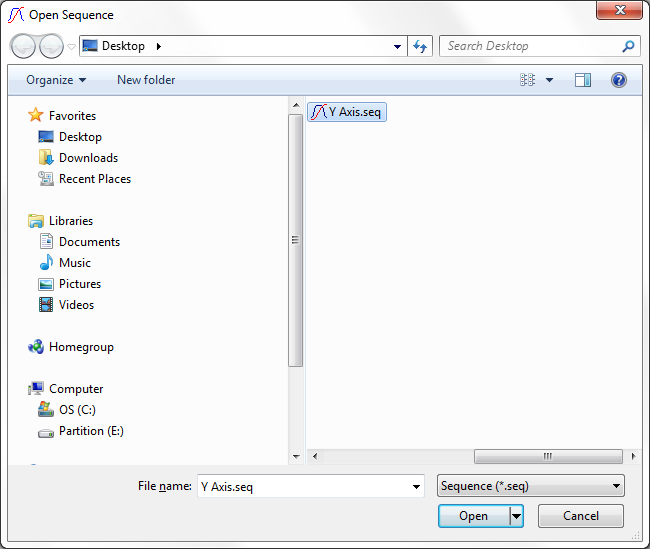
How Do I Open Seq Files
File Type 3NorPix StreamPix Sequence
| Developer | NorPix |
| Popularity | |
| Category | Video Files |
| Format | Binary |
.SEQ File Association 3
Colllection of images saved in a sequence that can be played back as a video file; created by NorPix digital video recording software; may be generated from a video camera recording or from individual frames captured by a frame grabber.
SEQ files can be exported to a standard video format, such as an .AVI or .MOV file, within the StreamPix application.
Programs that open SEQ files
File Type 4Tiertex Limited SEQ Video File
| Developer | Tiertex Design Studios Limited |
| Popularity | |
| Category | Video Files |
| Format | N/A |
.SEQ File Association 4
An SEQ file is a video file used by Flashback: The Quest for Identity, a video game for MS-DOS released in 1992. It is saved in the Tiertex Limited Sequence format and primarily used to store cutscene animations that appear during gameplay.
Since SEQ files are only used by the Flashback video game, you will most likely never encounter them unless you have installed the game from an MS-DOS CD-ROM onto your computer. Flashback was originally developed by Delphine Software for the Amiga gaming platform, then ported to MS-DOS by Tiertex Design Studios Limited and made available via a CD-ROM.
Tiertex Design Studios Limited is a British video game developer founded in 1986. They released games throughout the 1980s, 1990s, and 2000s for various platforms, such as Atari, Commodore 64, Sega Genesis, Game Gear, Game Boy, Super Nintendo, Game Boy Color, and Game Boy Advance. Tiertex Design Studios Limited ceased in 2003.
How do I open a SEQ file?
Since SEQ files are very rare, there are few programs that support it. However, you can convert an SEQ file to a more common video format with FFmpeg, then open the converted file with a media player, such as Microsoft Windows Media Player or VLC media player.
Programs that open SEQ files
Linux kernel seq_file HOWTO
Randy Dunlap <rddunlap@osdl.org>
v0: 2003-02-22
v1: 2003-03-14
Parts of this seq_file HOWTO were contributed by Andries Brouwer (aeb%win!tue!nl).
[Another seq_file reference is 'Driver porting: The seq_file interface' at <http://lwn.net/Articles/22355/>, which is part of the LWN.net series 'Porting Drivers to 2.5' that is located at <http://lwn.net/Articles/driver-porting/>.]
Introduction
The 'seq_file' interface to the /proc filesystem was introduced in Linux 2.4.15-pre3 and Linux 2.4.13-ac8. It provides a safer interface to the /proc filesystem than previous procfs methods because it protects against overflow of the output buffer and easily handles procfs files that are larger than one page. It also provides methods for traversing a list of kernel items and iterating on that list. It provides procfs output facilities that are less error-prone than the previous procfs interfaces.
Overview:
seq_file operates by using 'pull' methods, pulling or asking for data from seq_file operations methods, whereas the previous procfs methods pushed data into output buffers.
seq_file Creation and Data Structures
A seq_file-type /proc file is created by using create_proc_entry() and setting the resulting proc_dir_entry->proc_fops pointer to the desired struct file_operations. E.g. (from linux/mm/swapfile.c):
struct file_operations for the seq_file-type proc file describes 4 I/O methods, e.g.:
The last 3 are reusable seq_file-supplied methods. The open method is what must be supplied for each proc file, and that open()function only needs to call seq_open() with a pointer to a struct seq_operations descriptor. E.g. (still from linux/mm/swapfile.c):
struct seq_file seq_operations swaps_op supplies 4 methods for producing seq_file output: start(), next(), stop(), and show(). These are described below. The structure typically looks like:
seq_file Methods
The seq_file routines never take any locks between the ->open() and ->stop() functions, so seq_file callers are free to use anything -- spinlocks, etc.
The seq_file interface does require more data structures to be setup to point to methods that are used during seq_file access. In return for this, you (we) get much safer /proc output methods. These four methods are in struct seq_operations:
The .start method is used to initialize data for walking through a list of kernel items. This list can be an array, a linked list, a hash table, etc. Its actual data type doesn't matter. This function should lock whatever needs to be locked for safety and return an entry by number (0 for the first entry). This method should also honor file offset semantics by using the 'loff_t *pos' (second) parameter. The 'entry number' value is passed to the stop, next, and show methods as the 'void *v' parameter. In case of error, return ERR_PTR(error_code).
If you need to show a header line or something, then return SEQ_START_TOKEN in your start() and recognise that in next() and show(). IOW, pos 0 will be the header line, and pos 1 will correspond to the first actual item on your list, and so on. See net/netlink/af_netlink.c for a simple example.
If there is any locking that needs to be done to iterate through the kernel list, the lock(s) can be acquired in the .start method. However, if the .show method is very time-consuming and the .show method lends itself to locking there, that may be a better place for it.
struct seq_file contains a 'void *private' that can be used by the struct seq_operations functions to hold any private data that needs to be available to all of these related methods. For example, the .start method might allocate some memory and save its address in seq_file.private so that the .next and .show methods can use it, then the .stop method would free that memory.
The .stop method is called after the .next method has nothing more to do. This method is used for cleanups, unlocking, freeing resources, etc. The .stop method is always called if the .start method was called, even if the .start method fails, so that all cleanups can be done in .stop.
The .next method is the iterator for the items (list, array, table, etc.) that is being traversed for /proc file output. It advances to the next item of interest to be shown in the /proc output file and indicates when there are no more items by returning NULL or an error (like -ENOMEM or -EACCES). If there are more items to be shown, it returns the next element (entry) of the sequence by entry number.
The .show method is used to show an entry (write output to the /proc file) by using seq_...() as you would use stdio functions. It can write static headings or variable data into the seq_file output buffer. It uses seq_{putc, puts, printf, ...} to format the output (see below). In case of error, return a negative error_code; otherwise return 0.
Open Seq File
seq_file Output Routines
The seq_file output methods are:
What Can Open Seq Files
Simplified seq_file Methods

If you only need a single function entry (call) to produce all the desired proc-fs output, just use single_open() and single_release().
single_open() gets a parameter that is the 'show' function for the data that is to be written to /proc. The 'show' function does everything that is needed to write the data, all in one function call. This is useful either for writing small amounts of data to /proc, for cases in which the output is not iterative, or for cases in which recursion is more appropriate, since the non-single methods don't fit well with recursive techniques. Examples of appropriate uses of single_open() 'show' functions are:
How To Open Seq File
CategoryDocs
